Generally, elbow pain occurs when adding too much weight or doing too many repetitions of a certain exercise, which slowly deteriorates the tendons in the elbow.
Although the causes of elbow pain are many and difficult to pin down, most cases can be corrected with a few simple changes to the training plan.
The elbow consists of a joint formed by the intersection of the humerus (upper arm bone), the radius (large forearm bone), and the ulna (small forearm bone). The point where these bones meet runs through tendons, ligaments, and muscles.
The elbow’s job is to allow the forearm to flex and extend. It is involved in the most common upper body exercises, so its proper functioning is essential. Therefore, discover what you must do to solve elbow pain in time and keep it healthy.

Guide to solving elbow pain
1. What are the causes of elbow pain?
There are two main causes of elbow pain, which are as follows:
1.1 Traumatic injuries
For example, if you are bench pressing, and suddenly excruciating pain appears in your elbow, you have likely ruptured or dislocated a tendon or ligament.
1.2 Repetitive stress injuries
If you suddenly start to develop elbow pain, you are probably dealing with a Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI). This type of injury is caused by wear and tear due to repeated movements and overuse. And they tend to get progressively worse over time for lack of appropriate measures in time.

2. Who is more likely to suffer from elbow pain?
People who practice sports disciplines or have training routines that require frequent use of the elbows are more prone. This is the reason why one in two high-level tennis players may develop elbow pain at some point in their careers. Also, changing from a sedentary lifestyle to one that includes sudden exercise is another common cause.
In addition, people who are engaged in jobs that involve constantly lifting, moving, and carrying things also have twice the risk of developing elbow pain than those with more sedentary jobs.

4. What is the difference between tendonitis and elbow tendinosis?
When the body is injured, it produces an inflammatory response to help repair the damage. This can cause tenderness, swelling, and pain. This usually goes away after several days or weeks of rest.
Tendinitis refers to inflammation of the tendon, and is often mistaken for another cause of pain called tendinosis. The latter refers to the gradual breakdown of the tendon over time.
Tendinosis tends to take much longer to heal than tendinitis. Compared to muscles, skin, and other tissues, tendons have fewer blood vessels so they don’t receive the same amount of oxygen and nutrients to heal, grow, and get stronger.
Premature tendinosis usually heals after 6 to 10 weeks of rest.
5. How to relieve elbow pain?
Many of the most common solutions for elbow pain , consists of ingesting non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Also, it is advisable to place cold and use medications called corticosteroids.
It is important to note that in most elbow complaints, a few days or weeks of rest are not enough. If your elbow has been bothering you for several weeks or months, it may take longer to heal.
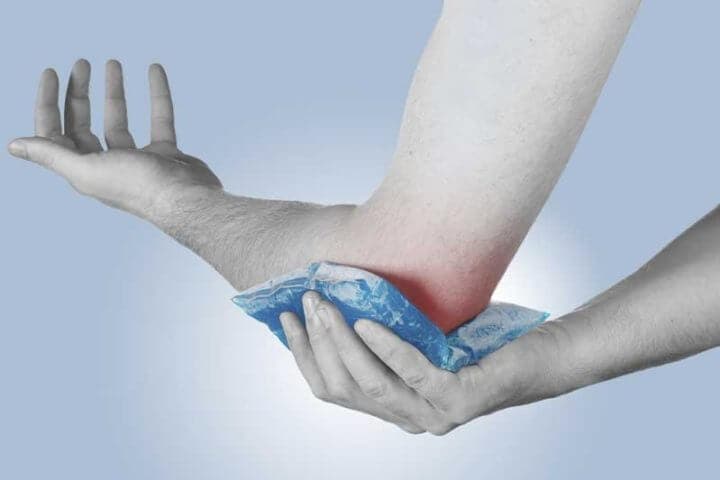
6. What other steps can I take to heal my elbow discomfort?
The solution is not necessarily to stop training altogether. It is best to gradually modify and reduce workouts allowing time for the elbow to heal. Therefore, it is advisable that you follow these steps to solve elbow pain :
6.1 Adjust the training plan
In many cases you will notice pain with certain exercises. For example, your elbow may hurt when you press the barbell bench press, but not when you do a dumbbell bench press. If that’s the case, then avoid exercises that hurt until your elbow heals.
Not only does this allow you to keep training, but research shows that staying active will help you recover faster.

6.2 Try physical therapy
Physical therapy involves the use of special exercises and devices to help people regain or preserve healthy movement. It can involve any number of different treatments, from massages to special movement exercises.
Different physical therapists also have methods and recommend different techniques, so it’s hard to say what works or not. So if resting your elbow doesn’t work, then try therapy. This is particularly true if you have been dealing with pain for a long time, and you continually find yourself with this injured joint.
6.3 Take the right supplements
Supplements do not heal injuries; But training properly, eating a healthy diet, and getting enough rest are all steps to fix an injury.
Most commonly marketed joint pain supplements, such as glucosamine, have been widely discredited. That said, there are safe and natural substances that science indicates help prevent and reduce elbow pain. These include fish oil, collagen, and grape seed extract.
Reference
- Legge, A. Have Elbow Pain? This Is Your 4-Step Guide to Fixing It. For Muscleforlife [Revised March 2018]
